理解 CUDA 記憶體使用#
創建於:2023年8月23日 | 最後更新於:2025年9月2日
為了除錯 CUDA 記憶體使用,PyTorch 提供了一種生成記憶體快照的方法,該方法可以在任何時間點記錄已分配 CUDA 記憶體的狀態,並可選擇記錄導致該快照的分配事件歷史。
生成的快照可以拖放到託管在 pytorch.org/memory_viz 上的互動式檢視器中,用於探索快照。
注意
本文件中描述的記憶體分析器和視覺化工具僅能檢視透過 PyTorch 分配器分配和管理的 CUDA 記憶體。直接從 CUDA API 分配的任何記憶體都將不會在 PyTorch 記憶體分析器中可見。
NCCL(用於 CUDA 裝置上的分散式通訊)是一個常見的庫,它會分配一些對 PyTorch 記憶體分析器不可見的 GPU 記憶體。有關更多資訊,請參閱 識別非 PyTorch 分配。
生成快照#
記錄快照的常用模式是啟用記憶體歷史記錄,執行要觀察的程式碼,然後將一個帶有序列化快照的檔案儲存下來。
# enable memory history, which will
# add tracebacks and event history to snapshots
torch.cuda.memory._record_memory_history()
run_your_code()
torch.cuda.memory._dump_snapshot("my_snapshot.pickle")
使用視覺化工具#
開啟 https://pytorch.com.tw/memory_viz,並將序列化的快照檔案拖放到視覺化工具中。該視覺化工具是一個在您本地計算機上執行的 JavaScript 應用程式。它不會上傳任何快照資料。
活動記憶體時間線#
活動記憶體時間線顯示了快照中特定 GPU 上隨時間推移的所有活動張量。可以透過平移/縮放圖表來檢視較小的分配。將滑鼠懸停在已分配的塊上,可以檢視該塊分配時的時間堆疊跟蹤,以及其地址等詳細資訊。可以透過調整詳細資訊滑塊來渲染更少的分配,從而在資料量很大時提高效能。
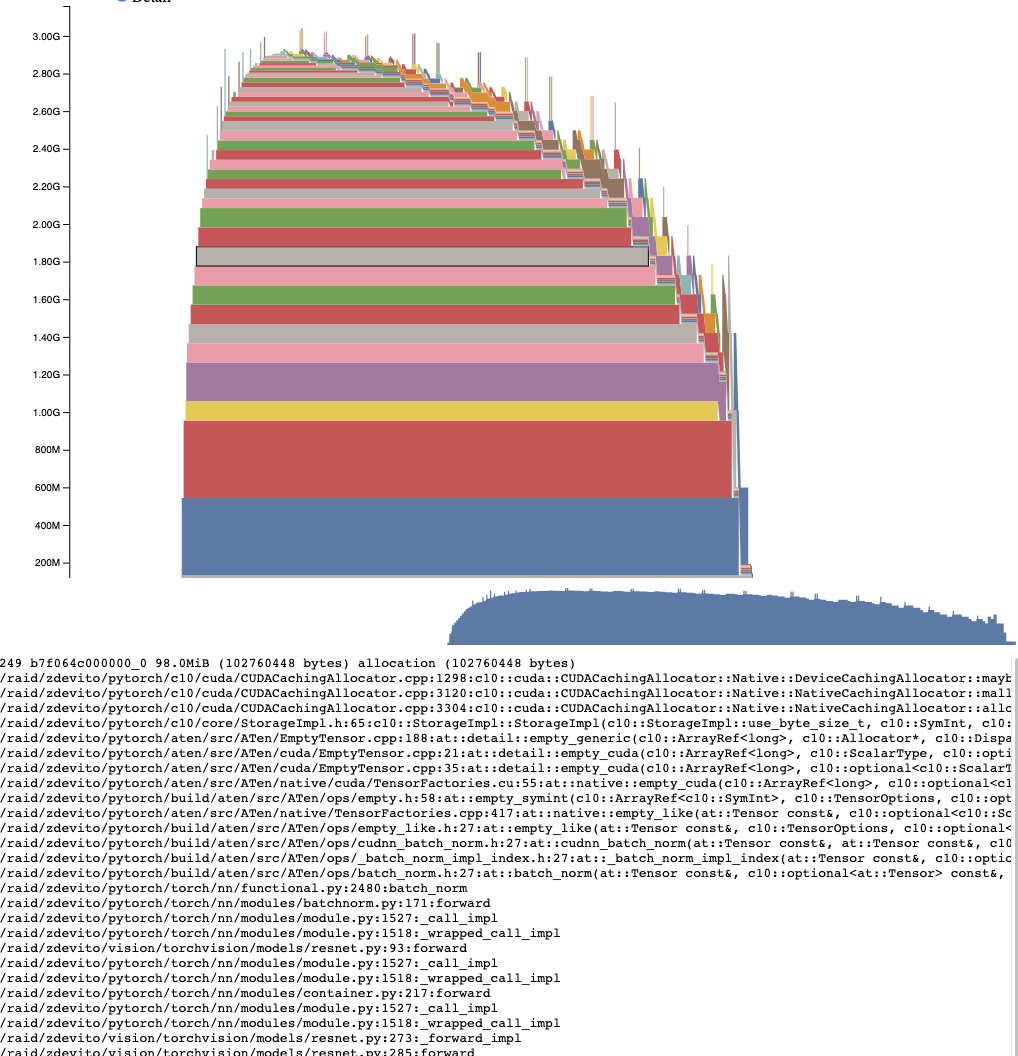
分配器狀態歷史#
分配器狀態歷史在左側的時間線上顯示了單個分配器事件。選擇時間線中的一個事件,即可看到該事件時分配器狀態的視覺化摘要。此摘要顯示了從 cudaMalloc 返回的每個單獨的段,以及它如何被分割成單獨的分配塊或空閒空間。將滑鼠懸停在段和塊上,可以看到記憶體分配時的時間堆疊跟蹤。將滑鼠懸停在事件上,可以看到事件發生時的時間堆疊跟蹤,例如張量被釋放時。記憶體不足錯誤會報告為 OOM 事件。檢視 OOM 期間的記憶體狀態可能會提供有關為什麼儘管仍有預留記憶體但分配失敗的洞察。
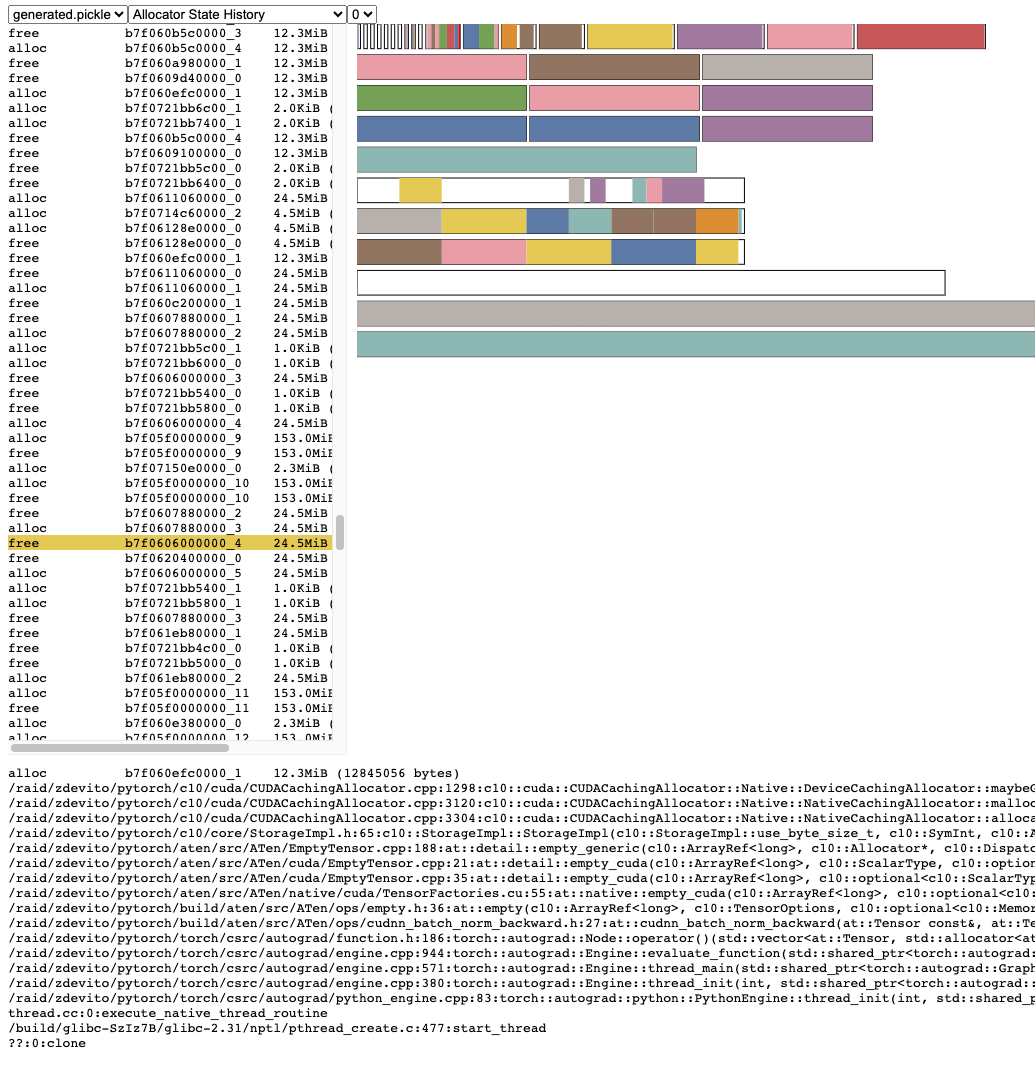
時間堆疊跟蹤資訊還報告了分配發生的地址。地址 b7f064c000000_0 指的是地址 7f064c000000 處的(塊),這是該地址被分配的“_0”次。可以在活動記憶體時間線中查詢此唯一字串,並在活動狀態歷史中搜索,以檢查張量分配或釋放時的記憶體狀態。
識別非 PyTorch 分配#
如果您懷疑 CUDA 記憶體是在 PyTorch 之外分配的,您可以使用 pynvml 包收集原始 CUDA 分配資訊,並將其與 pytorch 報告的分配進行比較。
要收集 PyTorch 外部的原始記憶體使用情況,請使用 device_memory_used()
import torch
device_idx = ...
print(torch.cuda.device_memory_used(device_idx))
快照 API 參考#
- torch.cuda.memory._record_memory_history(enabled='all', context='all', stacks='all', max_entries=9223372036854775807, device=None, clear_history=False, compile_context=False, global_record_annotations=False)[source]#
啟用記憶體分配相關的時間堆疊跟蹤記錄,以便您能夠弄清楚
torch.cuda.memory._snapshot()中的任何記憶體塊是如何分配的。除了為當前分配的記憶體和釋放的記憶體保留時間堆疊跟蹤外,此函式還將啟用對所有分配/釋放事件歷史記錄的記錄。
使用
torch.cuda.memory._snapshot()來檢索此資訊,並使用 _memory_viz.py 中的工具來視覺化快照。緩衝區行為#
啟用後,將儲存最多 max_entries 個 TraceEntry 例項。Python 跟蹤收集預設為 sys.maxsize,這意味著長時間執行或無限期執行的作業應設定合理的限制,以避免過多的記憶體使用。每個條目預計佔用幾 KB。
執行時間更長的工作流程或 max_entries 值較小的工作流程將僅儲存最後累積的 max_entries 個條目,這意味著新條目會覆蓋舊條目。
C++ 實現,供參考環形緩衝區實現
if (record_history) { if (alloc_trace->size() < alloc_trace_max_entries_) { alloc_trace->emplace_back(te); } else { (*alloc_trace)[alloc_trace_next++] = te; if (alloc_trace_next == alloc_trace_max_entries_) { alloc_trace_next = 0; } } }
延遲影響#
Python 跟蹤收集速度很快(每個跟蹤 2us),因此如果您預計將來需要除錯記憶體問題,可以考慮在生產作業中啟用此功能。
C++ 跟蹤收集速度也很快(約 50ns/幀),對於許多典型程式來說,這相當於每個跟蹤約 2us,但可能會因堆疊深度而異。
- 引數 enabled
None,停用記憶體歷史記錄。 “state”,保留當前已分配記憶體的資訊。 “all”,另外保留所有分配/釋放呼叫的歷史記錄。預設為“all”。
- 引數型別 enabled
Literal[None, “state”, “all”], optional
- 引數 context
None,不記錄任何回溯。 “state”,記錄當前已分配記憶體的回溯。 “alloc”,另外保留分配呼叫的回溯。 “all”,另外保留釋放呼叫的回溯。預設為“all”。
- 引數型別 context
Literal[None, “state”, “alloc”, “all”], optional
- 引數 stacks
“python”,包括 Python、TorchScript 和 Inductor 幀的回溯 “all”,另外包括 C++ 幀。預設為“all”。
- 引數型別 stacks
Literal[“python”, “all”], optional
- 引數 max_entries
在記錄的歷史記錄中保留最多 max_entries 個分配/釋放事件。
- 引數型別 max_entries
int, optional
- torch.cuda.memory._snapshot(device=None)[source]#
在呼叫時儲存 CUDA 記憶體狀態的快照。
狀態表示為具有以下結構的字典。
class Snapshot(TypedDict): segments: List[Segment] device_traces: List[List[TraceEntry]] class Segment(TypedDict): # Segments are memory returned from a cudaMalloc call. # The size of reserved memory is the sum of all Segments. # Segments are cached and reused for future allocations. # If the reuse is smaller than the segment, the segment # is split into more then one Block. # empty_cache() frees Segments that are entirely inactive. address: int total_size: int # cudaMalloc'd size of segment stream: int segment_type: Literal["small", "large"] # 'large' (>1MB) allocated_size: int # size of memory in use active_size: int # size of memory in use or in active_awaiting_free state blocks: List[Block] class Block(TypedDict): # A piece of memory returned from the allocator, or # current cached but inactive. size: int requested_size: int # size requested during malloc, may be smaller than # size due to rounding address: int state: Literal[ "active_allocated", # used by a tensor "active_awaiting_free", # waiting for another stream to finish using # this, then it will become free "inactive", ] # free for reuse frames: List[Frame] # stack trace from where the allocation occurred class Frame(TypedDict): filename: str line: int name: str class TraceEntry(TypedDict): # When `torch.cuda.memory._record_memory_history()` is enabled, # the snapshot will contain TraceEntry objects that record each # action the allocator took. action: Literal[ "alloc" # memory allocated "free_requested", # the allocated received a call to free memory "free_completed", # the memory that was requested to be freed is now # able to be used in future allocation calls "segment_alloc", # the caching allocator ask cudaMalloc for more memory # and added it as a segment in its cache "segment_free", # the caching allocator called cudaFree to return memory # to cuda possibly trying free up memory to # allocate more segments or because empty_caches was called "oom", # the allocator threw an OOM exception. 'size' is # the requested number of bytes that did not succeed "snapshot", # the allocator generated a memory snapshot # useful to coorelate a previously taken # snapshot with this trace ] addr: int # not present for OOM frames: List[Frame] size: int stream: int device_free: int # only present for OOM, the amount of # memory cuda still reports to be free
- 返回
快照字典物件
- torch.cuda.memory._dump_snapshot(filename='dump_snapshot.pickle')[source]#
將 torch.memory._snapshot() 字典的序列化版本儲存到檔案中。
此檔案可以被 pytorch.org/memory_viz 上的互動式快照檢視器開啟。
快照檔案大小與 max_entries 和每個條目的時間堆疊跟蹤深度成比例,每個條目為幾 KB。對於具有較大 max_entries 的長時間執行工作流程,這些檔案很容易達到 GB 級別。
- 引數
filename (str, optional) – 要建立的檔名。預設為“dump_snapshot.pickle”。
