torch.nested#
創建於: 2022年03月02日 | 最後更新於: 2025年06月14日
引言#
警告
PyTorch 中巢狀張量的 API 處於原型階段,將在不久的將來發生變化。
巢狀張量允許將形狀不規則的資料包含在內,並將其作為一個單一的張量進行操作。此類資料在底層以高效的打包表示形式儲存,同時暴露標準的 PyTorch 張量介面以應用操作。
巢狀張量的一個常見應用是表示各種領域中存在的變長序列資料的批次,例如不同的句子長度、影像大小以及音訊/影片片段長度。傳統上,此類資料是透過將序列填充到批次內的最大長度,對填充後的形式執行計算,然後進行掩碼以移除填充來處理的。這效率低下且容易出錯,巢狀張量的出現旨在解決這些問題。
呼叫巢狀張量操作的 API 與常規 torch.Tensor 的 API 沒有區別,允許與現有模型無縫整合,主要區別在於 輸入的構造。
由於這是一項原型功能,支援的操作集是有限的,但正在不斷增長。我們歡迎提交 issue、功能請求和貢獻。有關貢獻的更多資訊可以在 此 Readme 中找到。
構造#
注意
PyTorch 中存在兩種形式的巢狀張量,它們在構造時指定的佈局上有所區別。佈局可以是 torch.strided 或 torch.jagged。我們建議儘可能利用 torch.jagged 佈局。雖然它目前只支援一個不規則維度,但它具有更好的操作覆蓋率,正在積極開發中,並且與 torch.compile 整合良好。這些文件遵循此建議,並在全文中簡稱具有 torch.jagged 佈局的巢狀張量為“NJTs”。
構造很簡單,涉及將張量列表傳遞給 torch.nested.nested_tensor 建構函式。具有 torch.jagged 佈局的巢狀張量(又名“NJT”)支援單個不規則維度。此建構函式將根據下方 data_layout 部分所述的佈局,將輸入張量複製到一個打包的、連續的記憶體塊中。
>>> a, b = torch.arange(3), torch.arange(5) + 3
>>> a
tensor([0, 1, 2])
>>> b
tensor([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> print([component for component in nt])
[tensor([0, 1, 2]), tensor([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])]
列表中的每個張量必須具有相同的維數,但形狀沿單個維度可以不同。如果輸入元件的維度不匹配,建構函式將丟擲錯誤。
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128) # 2D tensor
>>> b = torch.randn(2, 50, 128) # 3D tensor
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
...
RuntimeError: When constructing a nested tensor, all tensors in list must have the same dim
在構造期間,可以透過常規關鍵字引數選擇 dtype、device 以及是否需要梯度。
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda", requires_grad=True)
>>> print([component for component in nt])
[tensor([0., 1., 2.], device='cuda:0',
grad_fn=<UnbindBackwardAutogradNestedTensor0>), tensor([3., 4., 5., 6., 7.], device='cuda:0',
grad_fn=<UnbindBackwardAutogradNestedTensor0>)]
torch.nested.as_nested_tensor 可用於保留傳遞給建構函式的張量的 autograd 歷史記錄。當使用此建構函式時,梯度將透過巢狀張量流回原始元件。請注意,此建構函式仍會將輸入元件複製到一個打包的、連續的記憶體塊中。
>>> a = torch.randn(12, 512, requires_grad=True)
>>> b = torch.randn(23, 512, requires_grad=True)
>>> nt = torch.nested.as_nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt.sum().backward()
>>> a.grad
tensor([[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
...,
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.]])
>>> b.grad
tensor([[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
...,
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.]])
上述函式都建立了連續的 NJT,其中分配了一塊記憶體來儲存底層元件的打包形式(有關更多詳細資訊,請參見下方 data_layout 部分)。
還可以透過預先存在的填充密集張量建立非連續的 NJT 檢視,從而避免記憶體分配和複製。 torch.nested.narrow() 是實現此目的的工具。
>>> padded = torch.randn(3, 5, 4)
>>> seq_lens = torch.tensor([3, 2, 5], dtype=torch.int64)
>>> nt = torch.nested.narrow(padded, dim=1, start=0, length=seq_lens, layout=torch.jagged)
>>> nt.shape
torch.Size([3, j1, 4])
>>> nt.is_contiguous()
False
請注意,巢狀張量充當原始填充密集張量的檢視,引用相同的記憶體而不進行復制/分配。非連續 NJT 的操作支援略有限制,因此如果您遇到支援差距,始終可以使用 contiguous() 轉換為連續 NJT。
資料佈局和形狀#
為了提高效率,巢狀張量通常將它們的張量元件打包到一個連續的記憶體塊中,並維護附加的元資料來指定批次項的邊界。對於 torch.jagged 佈局,連續的記憶體塊儲存在 values 元件中,offsets 元件用於區分不規則維度的批次項邊界。
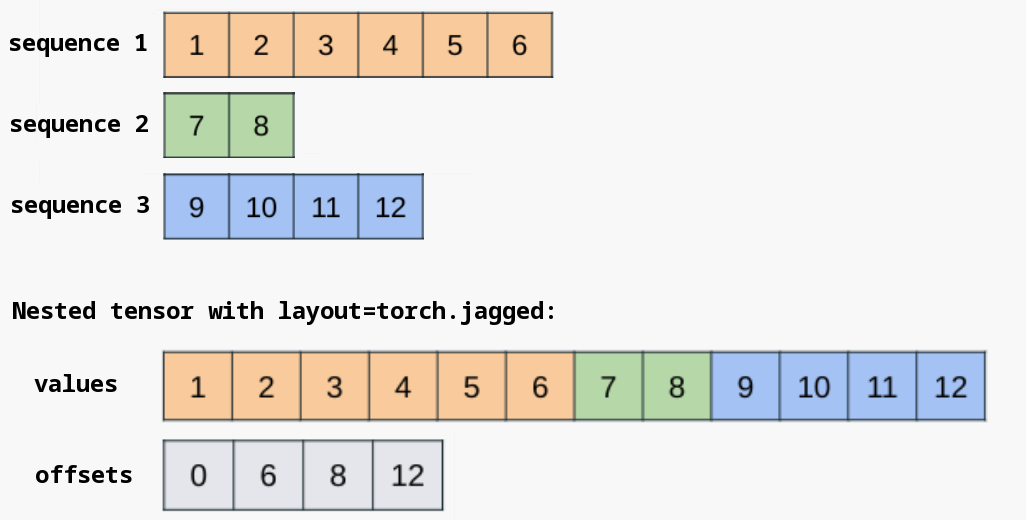
必要時可以直接訪問底層的 NJT 元件。
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128) # text 1
>>> b = torch.randn(32, 128) # text 2
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt.values().shape # note the "packing" of the ragged dimension; no padding needed
torch.Size([82, 128])
>>> nt.offsets()
tensor([ 0, 50, 82])
直接從不規則的 values 和 offsets 成分構造 NJT 也可能有用;torch.nested.nested_tensor_from_jagged() 建構函式用於此目的。
>>> values = torch.randn(82, 128)
>>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 50, 82], dtype=torch.int64)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor_from_jagged(values=values, offsets=offsets)
NJT 具有明確定義的形狀,其維度比其元件的維度大 1。不規則維度的底層結構由一個符號值表示(下方示例中的 j1)。
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128)
>>> b = torch.randn(32, 128)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt.dim()
3
>>> nt.shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 128])
NJT 必須具有相同的不規則結構才能相互相容。例如,要執行涉及兩個 NJT 的二元運算,不規則結構必須匹配(即它們在形狀中必須具有相同的 不規則形狀符號)。在細節上,每個符號對應一個精確的 offsets 張量,因此兩個 NJT 必須擁有相同的 offsets 張量才能相互相容。
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128)
>>> b = torch.randn(32, 128)
>>> nt1 = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt2 = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt1.offsets() is nt2.offsets()
False
>>> nt3 = nt1 + nt2
RuntimeError: cannot call binary pointwise function add.Tensor with inputs of shapes (2, j2, 128) and (2, j3, 128)
在上面的示例中,即使兩個 NJT 的概念形狀相同,它們也不共享對同一 offsets 張量的引用,因此它們的形狀不同,並且不相容。我們認識到這種行為是不直觀的,並且正在努力為巢狀張量的 beta 版本放寬此限制。有關解決方法,請參閱本文件的 故障排除 部分。
除了 offsets 元資料外,NJT 還可以計算並快取其元件的最小和最大序列長度,這對於呼叫特定核心(例如 SDPA)可能很有用。目前沒有公共 API 來訪問這些,但對於 beta 版本來說,這種情況將會改變。
支援的操作#
本節包含您可能覺得有用的常見巢狀張量操作列表。它並不詳盡,因為 PyTorch 中有數千種操作。雖然今天巢狀張量支援其中的一個可觀子集,但全面支援是一項艱鉅的任務。巢狀張量的理想狀態是完全支援非巢狀張量可用的所有 PyTorch 操作。為了幫助我們實現這一目標,請考慮
檢視巢狀張量元件#
unbind() 允許您檢索巢狀張量元件的檢視。
>>> import torch
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> b = torch.randn(3, 3)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> nt.unbind()
(tensor([[-0.9916, -0.3363, -0.2799],
[-2.3520, -0.5896, -0.4374]]), tensor([[-2.0969, -1.0104, 1.4841],
[ 2.0952, 0.2973, 0.2516],
[ 0.9035, 1.3623, 0.2026]]))
>>> nt.unbind()[0] is not a
True
>>> nt.unbind()[0].mul_(3)
tensor([[ 3.6858, -3.7030, -4.4525],
[-2.3481, 2.0236, 0.1975]])
>>> nt.unbind()
(tensor([[-2.9747, -1.0089, -0.8396],
[-7.0561, -1.7688, -1.3122]]), tensor([[-2.0969, -1.0104, 1.4841],
[ 2.0952, 0.2973, 0.2516],
[ 0.9035, 1.3623, 0.2026]]))
請注意,nt.unbind()[0] 不是副本,而是底層記憶體的切片,它代表巢狀張量的第一個條目或元件。
轉換為/從填充張量#
torch.nested.to_padded_tensor() 將 NJT 轉換為具有指定填充值的填充密集張量。不規則維度將被填充到最大序列長度的大小。
>>> import torch
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> b = torch.randn(6, 3)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> padded = torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(nt, padding=4.2)
>>> padded
tensor([[[ 1.6107, 0.5723, 0.3913],
[ 0.0700, -0.4954, 1.8663],
[ 4.2000, 4.2000, 4.2000],
[ 4.2000, 4.2000, 4.2000],
[ 4.2000, 4.2000, 4.2000],
[ 4.2000, 4.2000, 4.2000]],
[[-0.0479, -0.7610, -0.3484],
[ 1.1345, 1.0556, 0.3634],
[-1.7122, -0.5921, 0.0540],
[-0.5506, 0.7608, 2.0606],
[ 1.5658, -1.1934, 0.3041],
[ 0.1483, -1.1284, 0.6957]]])
這可以作為一種解決方法來處理 NJT 支援的差距,但理想情況下,應儘可能避免此類轉換,以獲得最佳記憶體使用和效能,因為更高效的巢狀張量佈局不會具體化填充。
反向轉換可以使用 torch.nested.narrow() 完成,它將不規則結構應用於給定的密集張量以生成 NJT。請注意,預設情況下,此操作不會複製底層資料,因此輸出的 NJT 通常是非連續的。如果需要連續的 NJT,明確呼叫 contiguous() 可能會有用。
>>> padded = torch.randn(3, 5, 4)
>>> seq_lens = torch.tensor([3, 2, 5], dtype=torch.int64)
>>> nt = torch.nested.narrow(padded, dim=1, length=seq_lens, layout=torch.jagged)
>>> nt.shape
torch.Size([3, j1, 4])
>>> nt = nt.contiguous()
>>> nt.shape
torch.Size([3, j2, 4])
形狀操作#
巢狀張量支援廣泛的形狀操作,包括檢視。
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 6)
>>> b = torch.randn(4, 6)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> nt.shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 6])
>>> nt.unsqueeze(-1).shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 6, 1])
>>> nt.unflatten(-1, [2, 3]).shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 2, 3])
>>> torch.cat([nt, nt], dim=2).shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 12])
>>> torch.stack([nt, nt], dim=2).shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 2, 6])
>>> nt.transpose(-1, -2).shape
torch.Size([2, 6, j1])
注意力機制#
由於變長序列是注意力機制的常見輸入,巢狀張量支援重要的注意力運算元 縮放點積注意力 (SDPA) 和 FlexAttention。有關 NJT 與 SDPA 用法的示例,請參見 此處;有關 NJT 與 FlexAttention 用法的示例,請參見 此處。
與 torch.compile 的用法#
NJT 被設計用於與 torch.compile() 結合使用以獲得最佳效能,並且我們始終建議在可能的情況下使用 torch.compile() 配合 NJT 使用。NJT 可以直接使用,並且在作為編譯函式的輸入或模組,或在函式內部內聯例項化時,都可以無縫工作,無需圖中斷。
注意
If you're not able to utilize ``torch.compile()`` for your use case, performance and memory
usage may still benefit from the use of NJTs, but it's not as clear-cut whether this will be
the case. It is important that the tensors being operated on are large enough so the
performance gains are not outweighed by the overhead of python tensor subclasses.
>>> import torch
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> b = torch.randn(4, 3)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> def f(x): return x.sin() + 1
...
>>> compiled_f = torch.compile(f, fullgraph=True)
>>> output = compiled_f(nt)
>>> output.shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 3])
>>> def g(values, offsets): return torch.nested.nested_tensor_from_jagged(values, offsets) * 2.
...
>>> compiled_g = torch.compile(g, fullgraph=True)
>>> output2 = compiled_g(nt.values(), nt.offsets())
>>> output2.shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 3])
請注意,NJT 支援 動態形狀,以避免因不規則結構變化而引起的非必要重編譯。
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> b = torch.randn(4, 3)
>>> c = torch.randn(5, 3)
>>> d = torch.randn(6, 3)
>>> nt1 = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> nt2 = torch.nested.nested_tensor([c, d], layout=torch.jagged)
>>> def f(x): return x.sin() + 1
...
>>> compiled_f = torch.compile(f, fullgraph=True)
>>> output1 = compiled_f(nt1)
>>> output2 = compiled_f(nt2) # NB: No recompile needed even though ragged structure differs
如果您在使用 NJT + torch.compile 時遇到問題或遇到晦澀難懂的錯誤,請提交 PyTorch issue。在 torch.compile 中對子類進行全面支援是一項長期工作,目前可能還有一些不完善之處。
故障排除#
本節包含在使用巢狀張量時可能遇到的常見錯誤,以及這些錯誤的根本原因和建議的解決方法。
未實現的運算元#
隨著巢狀張量操作支援的增長,此錯誤變得越來越少見,但考慮到 PyTorch 中存在數千種操作,今天仍有可能遇到它。
NotImplementedError: aten.view_as_real.default
錯誤很簡單;我們還沒有為這個特定操作新增操作支援。如果您願意,可以 自己貢獻 一個實現,或者直接 請求 我們在未來的 PyTorch 版本中新增對該操作的支援。
不規則結構不相容#
RuntimeError: cannot call binary pointwise function add.Tensor with inputs of shapes (2, j2, 128) and (2, j3, 128)
當呼叫一個對多個具有不相容不規則結構的 NJT 進行操作的運算元時,會發生此錯誤。目前,要求輸入的 NJT 具有完全相同的 offsets 成分,才能具有相同的符號不規則結構符號(例如 j1)。
作為此情況的解決方法,可以直接從 values 和 offsets 成分構造 NJT。當兩個 NJT 都引用相同的 offsets 成分時,它們被認為具有相同的不規則結構,因此相容。
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128)
>>> b = torch.randn(32, 128)
>>> nt1 = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> nt2 = torch.nested.nested_tensor_from_jagged(values=torch.randn(82, 128), offsets=nt1.offsets())
>>> nt3 = nt1 + nt2
>>> nt3.shape
torch.Size([2, j1, 128])
torch.compile 中的資料相關操作#
torch._dynamo.exc.Unsupported: data dependent operator: aten._local_scalar_dense.default; to enable, set torch._dynamo.config.capture_scalar_outputs = True
呼叫在 torch.compile 中執行資料相關操作的運算元時會發生此錯誤;這通常發生在需要檢查 NJT 的 offsets 的值的運算元上,以確定輸出形狀。例如
>>> a = torch.randn(50, 128)
>>> b = torch.randn(32, 128)
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], layout=torch.jagged, dtype=torch.float32)
>>> def f(nt): return nt.chunk(2, dim=0)[0]
...
>>> compiled_f = torch.compile(f, fullgraph=True)
>>> output = compiled_f(nt)
在此示例中,對 NJT 的批次維度呼叫 chunk() 需要檢查 NJT 的 offsets 資料,以區分打包的不規則維度中的批次項邊界。作為解決方法,可以設定幾個 torch.compile 標誌
>>> torch._dynamo.config.capture_dynamic_output_shape_ops = True
>>> torch._dynamo.config.capture_scalar_outputs = True
在設定了這些標誌後,如果仍然看到資料相關運算元錯誤,請提交 PyTorch issue。 torch.compile() 的這一領域仍在大力開發中,NJT 支援的某些方面可能尚不完善。
貢獻#
如果您想為巢狀張量的開發做出貢獻,最有效的方式之一是為當前不支援的 PyTorch 操作新增巢狀張量支援。這個過程通常包括幾個簡單的步驟:
確定要新增的操作名稱;這應該是類似於
aten.view_as_real.default的名稱。此操作的簽名可以在aten/src/ATen/native/native_functions.yaml中找到。在
torch/nested/_internal/ops.py中註冊操作實現,遵循那裡為其他操作建立的模式。使用native_functions.yaml中的簽名進行模式驗證。
實現操作的最常見方法是解開 NJT 到其元件,對底層 values 緩衝區重新排程操作,並將相關的 NJT 元資料(包括 offsets)傳播到新的輸出 NJT。如果操作的輸出預期具有與輸入不同的形狀,則必須計算新的 offsets 等元資料。
當操作應用於批次維度或不規則維度時,這些技巧可以幫助快速獲得可行的實現:
對於非批次wise 操作,基於
unbind()的回退應該有效。對於不規則維度的操作,可以考慮轉換為填充密集張量,並選擇一個不會負面影響輸出的填充值,執行操作,然後轉換回 NJT。在
torch.compile中,這些轉換可以被融合,以避免具體化填充的中間結果。
構造和轉換函式的詳細文件#
- torch.nested.nested_tensor(tensor_list, *, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)[source]#
從
tensor_list(一個張量列表)構造一個沒有 autograd 歷史記錄的巢狀張量(也稱為“葉張量”,請參閱 Autograd 機制)。- 引數
tensor_list (List[array_like]) – 一個張量列表,或任何可以傳遞給 torch.tensor 的內容,
維度。 (列表中的每個元素具有相同的) –
- 關鍵字引數
dtype (
torch.dtype, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望型別。預設值:如果為 None,則與列表中的最左邊張量具有相同的torch.dtype。layout (
torch.layout, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望佈局。僅支援 strided 和 jagged 佈局。預設值:如果為 None,則為 strided 佈局。device (
torch.device, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望裝置。預設值:如果為 None,則與列表中的最左邊張量具有相同的torch.devicerequires_grad (bool, optional) – 如果 autograd 應該記錄返回的巢狀張量上的操作。預設值:
False。pin_memory (bool, optional) – 如果設定,返回的巢狀張量將被分配到固定記憶體中。僅適用於 CPU 張量。預設值:
False。
- 返回型別
示例
>>> a = torch.arange(3, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) >>> b = torch.arange(5, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) >>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([a, b], requires_grad=True) >>> nt.is_leaf True
- torch.nested.nested_tensor_from_jagged(values, offsets=None, lengths=None, jagged_dim=None, min_seqlen=None, max_seqlen=None)[source]#
從給定的不規則元件構造一個不規則佈局的巢狀張量。不規則佈局包含一個必需的 values 緩衝區,其中不規則維度被打包成單個維度。offsets/lengths 元資料決定了該維度如何被分割成批次元素,並期望它們被分配在與 values 緩衝區相同的裝置上。
- 期望的元資料格式
offsets: 位於打包維度內的索引,將打包維度分割成大小不等的批次元素。例如:[0, 2, 3, 6] 表示一個大小為 6 的打包不規則維度應被概念上分割成長度為 [2, 1, 3] 的批次元素。請注意,為了方便核心(即 shape batch_size + 1)操作,需要開始和結束偏移量。
lengths: 批次元素的長度,shape == batch_size。例如:[2, 1, 3] 表示一個大小為 6 的打包不規則維度應被概念上分割成長度為 [2, 1, 3] 的批次元素。
請注意,同時提供 offsets 和 lengths 會很有用。這描述了一個帶有“空隙”的巢狀張量,其中 offsets 指示每個批次項的起始位置,而 length 指定元素的總數(參見下面的示例)。
返回的不規則佈局巢狀張量將是輸入 values 張量的檢視。
- 引數
values (
torch.Tensor) – 底層緩衝區,形狀為 (sum_B(*), D_1, …, D_N)。不規則維度被打包成單個維度,使用 offsets/lengths 元資料區分批次元素。offsets (optional
torch.Tensor) – 不規則維度的偏移量,形狀為 B + 1。lengths (optional
torch.Tensor) – 批次元素的長度,形狀為 B。jagged_dim (optional python:int) – 指示 values 中哪個維度是不規則打包維度。必須大於等於 1,因為批次維度(dim=0)不能是不規則的。如果為 None,則設定為 dim=1(即批次維度之後的第一個維度)。預設值:None
min_seqlen (optional python:int) – 如果設定,則使用指定的值作為返回巢狀張量的快取最小序列長度。這可以作為一種有用的替代方案來按需計算此值,可能避免 GPU -> CPU 同步。預設值:None
max_seqlen (optional python:int) – 如果設定,則使用指定的值作為返回巢狀張量的快取最大序列長度。這可以作為一種有用的替代方案來按需計算此值,可能避免 GPU -> CPU 同步。預設值:None
- 返回型別
示例
>>> values = torch.randn(12, 5) >>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 3, 5, 6, 10, 12]) >>> nt = nested_tensor_from_jagged(values, offsets) >>> # 3D shape with the middle dimension jagged >>> nt.shape torch.Size([5, j2, 5]) >>> # Length of each item in the batch: >>> offsets.diff() tensor([3, 2, 1, 4, 2]) >>> values = torch.randn(6, 5) >>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 2, 3, 6]) >>> lengths = torch.tensor([1, 1, 2]) >>> # NT with holes >>> nt = nested_tensor_from_jagged(values, offsets, lengths) >>> a, b, c = nt.unbind() >>> # Batch item 1 consists of indices [0, 1) >>> torch.equal(a, values[0:1, :]) True >>> # Batch item 2 consists of indices [2, 3) >>> torch.equal(b, values[2:3, :]) True >>> # Batch item 3 consists of indices [3, 5) >>> torch.equal(c, values[3:5, :]) True
- torch.nested.as_nested_tensor(ts, dtype=None, device=None, layout=None)[source]#
構造一個保留 autograd 歷史記錄的巢狀張量,它來自一個張量或一個張量列表/元組。
如果傳入巢狀張量,它將被直接返回,除非裝置/dtype/佈局不同。請注意,轉換裝置/dtype 將導致複製,而轉換佈局在此函式中目前不受支援。
如果傳入非巢狀張量,它將被視為具有一致大小的元件批次。如果傳入的裝置/dtype 與輸入的裝置/dtype 不同,或者如果輸入是非連續的,則會發生複製。否則,將直接使用輸入的儲存。
如果提供張量列表,在構造巢狀張量時,列表中的張量始終會被複制。
- 引數
ts (Tensor 或 List[Tensor] 或 Tuple[Tensor]) – 要視為巢狀張量的張量,或具有相同 ndim 的張量列表/元組
- 關鍵字引數
dtype (
torch.dtype, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望型別。預設值:如果為 None,則與列表中的最左邊張量具有相同的torch.dtype。device (
torch.device, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望裝置。預設值:如果為 None,則與列表中的最左邊張量具有相同的torch.devicelayout (
torch.layout, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望佈局。僅支援 strided 和 jagged 佈局。預設值:如果為 None,則為 strided 佈局。
- 返回型別
示例
>>> a = torch.arange(3, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) >>> b = torch.arange(5, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) >>> nt = torch.nested.as_nested_tensor([a, b]) >>> nt.is_leaf False >>> fake_grad = torch.nested.nested_tensor([torch.ones_like(a), torch.zeros_like(b)]) >>> nt.backward(fake_grad) >>> a.grad tensor([1., 1., 1.]) >>> b.grad tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]) >>> c = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True) >>> nt2 = torch.nested.as_nested_tensor(c)
- torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(input, padding, output_size=None, out=None) Tensor#
透過填充
input巢狀張量返回一個新的(非巢狀)張量。前面的條目將用巢狀資料填充,而後面的條目將進行填充。警告
to_padded_tensor()始終複製底層資料,因為巢狀張量和非巢狀張量在記憶體佈局上有所不同。- 引數
padding (float) – 後面條目的填充值。
- 關鍵字引數
示例
>>> nt = torch.nested.nested_tensor([torch.randn((2, 5)), torch.randn((3, 4))]) nested_tensor([ tensor([[ 1.6862, -1.1282, 1.1031, 0.0464, -1.3276], [-1.9967, -1.0054, 1.8972, 0.9174, -1.4995]]), tensor([[-1.8546, -0.7194, -0.2918, -0.1846], [ 0.2773, 0.8793, -0.5183, -0.6447], [ 1.8009, 1.8468, -0.9832, -1.5272]]) ]) >>> pt_infer = torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(nt, 0.0) tensor([[[ 1.6862, -1.1282, 1.1031, 0.0464, -1.3276], [-1.9967, -1.0054, 1.8972, 0.9174, -1.4995], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]], [[-1.8546, -0.7194, -0.2918, -0.1846, 0.0000], [ 0.2773, 0.8793, -0.5183, -0.6447, 0.0000], [ 1.8009, 1.8468, -0.9832, -1.5272, 0.0000]]]) >>> pt_large = torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(nt, 1.0, (2, 4, 6)) tensor([[[ 1.6862, -1.1282, 1.1031, 0.0464, -1.3276, 1.0000], [-1.9967, -1.0054, 1.8972, 0.9174, -1.4995, 1.0000], [ 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000], [ 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], [[-1.8546, -0.7194, -0.2918, -0.1846, 1.0000, 1.0000], [ 0.2773, 0.8793, -0.5183, -0.6447, 1.0000, 1.0000], [ 1.8009, 1.8468, -0.9832, -1.5272, 1.0000, 1.0000], [ 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]]]) >>> pt_small = torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(nt, 2.0, (2, 2, 2)) RuntimeError: Value in output_size is less than NestedTensor padded size. Truncation is not supported.
- torch.nested.masked_select(tensor, mask)[source]#
給定一個 strided 張量輸入和一個 strided mask,構造一個巢狀張量,結果的不規則佈局巢狀張量將保留 mask 等於 True 的值。mask 的維度被保留並用 offsets 表示,這與
masked_select()不同,後者將輸出摺疊到一維張量。Args: tensor (
torch.Tensor): 用於從其中構造不規則佈局巢狀張量的 strided 張量。 mask (torch.Tensor): 應用於 tensor 輸入的 strided mask 張量示例
>>> tensor = torch.randn(3, 3) >>> mask = torch.tensor([[False, False, True], [True, False, True], [False, False, True]]) >>> nt = torch.nested.masked_select(tensor, mask) >>> nt.shape torch.Size([3, j4]) >>> # Length of each item in the batch: >>> nt.offsets().diff() tensor([1, 2, 1]) >>> tensor = torch.randn(6, 5) >>> mask = torch.tensor([False]) >>> nt = torch.nested.masked_select(tensor, mask) >>> nt.shape torch.Size([6, j5]) >>> # Length of each item in the batch: >>> nt.offsets().diff() tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
- 返回型別
- torch.nested.narrow(tensor, dim, start, length, layout=torch.strided)[source]#
從
tensor(一個 strided 張量)構造一個巢狀張量(可能是檢視)。這遵循與 torch.Tensor.narrow 類似語義,其中在dim維度上,新的巢狀張量只顯示區間 [start, start+length) 中的元素。由於巢狀表示允許每個“行”在該維度上具有不同的 start 和 length,因此start和length也可以是形狀為 tensor.shape[0] 的張量。根據您為巢狀張量使用的佈局,會有一些差異。如果使用 strided 佈局,torch.narrow 將把窄化資料複製到一個具有 strided 佈局的連續 NT 中,而 jagged 佈局的 narrow() 將建立您原始 strided 張量的非連續檢視。這種特定的表示形式對於表示 Transformer 模型中的 kv-caches 非常有用,因為專門的 SDPA 核心可以輕鬆處理該格式,從而提高效能。
- 引數
tensor (
torch.Tensor) – 一個 strided 張量,如果使用 jagged 佈局,它將被用作巢狀張量的底層資料,或者對於 strided 佈局將被複制。dim (int) – narrow 操作應用的維度。對於 jagged 佈局僅支援 dim=1,而 strided 支援所有維度
start (Union[int,
torch.Tensor]) – narrow 操作的起始元素length (Union[int,
torch.Tensor]) – narrow 操作中包含的元素數量
- 關鍵字引數
layout (
torch.layout, optional) – 返回的巢狀張量的期望佈局。僅支援 strided 和 jagged 佈局。預設值:如果為 None,則為 strided 佈局。- 返回型別
示例
>>> starts = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=torch.int64) >>> lengths = torch.tensor([3, 2, 2, 1, 5], dtype=torch.int64) >>> narrow_base = torch.randn(5, 10, 20) >>> nt_narrowed = torch.nested.narrow(narrow_base, 1, starts, lengths, layout=torch.jagged) >>> nt_narrowed.is_contiguous() False
