


注意
轉到末尾 下載完整的示例程式碼。
ONNX 簡介 || 將 PyTorch 模型匯出為 ONNX || 擴充套件 ONNX 匯出器運算元支援 || 將包含控制流的模型匯出為 ONNX
將 PyTorch 模型匯出為 ONNX#
建立日期:2023 年 10 月 4 日 | 最後更新日期:2025 年 7 月 11 日 | 最後驗證日期:2024 年 11 月 5 日
作者:Ti-Tai Wang, Justin Chu, Thiago Crepaldi。
注意
從 PyTorch 2.5 開始,有兩種 ONNX 匯出器選項可用。* torch.onnx.export(..., dynamo=True) 是推薦的匯出器,它利用 torch.export 和 Torch FX 進行圖捕獲。* torch.onnx.export 是依賴已棄用的 TorchScript 的舊方法,不再推薦使用。
在 60 分鐘速成班 中,我們有機會對 PyTorch 進行高層次的學習,並訓練了一個小型神經網路來對影像進行分類。在本教程中,我們將在此基礎上進一步介紹如何使用 torch.onnx.export(..., dynamo=True) ONNX 匯出器將 PyTorch 定義的模型轉換為 ONNX 格式。
雖然 PyTorch 在模型開發迭代方面表現出色,但模型可以以不同的格式部署到生產環境,包括 ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange)!
ONNX 是一種靈活的開放標準格式,用於表示機器學習模型。標準化的機器學習表示允許它們在各種硬體平臺和執行時環境中執行,從大規模雲端超級計算機到資源受限的邊緣裝置,例如你的網頁瀏覽器和手機。
在本教程中,我們將學習如何
安裝必要的依賴項。
編寫一個簡單的影像分類器模型。
將模型匯出為 ONNX 格式。
將 ONNX 模型儲存到檔案中。
使用 Netron 視覺化 ONNX 模型圖。
使用 ONNX Runtime 執行 ONNX 模型
比較 PyTorch 的結果與 ONNX Runtime 的結果。
1. 安裝必要的依賴項#
由於 ONNX 匯出器使用 onnx 和 onnxscript 將 PyTorch 運算元轉換為 ONNX 運算元,因此我們需要安裝它們。
pip install --upgrade onnx onnxscript
3. 將模型匯出為 ONNX 格式#
現在我們已經定義了模型,我們需要例項化它並建立一個隨機的 32x32 輸入。接下來,我們可以將模型匯出為 ONNX 格式。
torch_model = ImageClassifierModel()
# Create example inputs for exporting the model. The inputs should be a tuple of tensors.
example_inputs = (torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32),)
onnx_program = torch.onnx.export(torch_model, example_inputs, dynamo=True)
[torch.onnx] Obtain model graph for `ImageClassifierModel([...]` with `torch.export.export(..., strict=False)`...
[torch.onnx] Obtain model graph for `ImageClassifierModel([...]` with `torch.export.export(..., strict=False)`... ✅
[torch.onnx] Run decomposition...
[torch.onnx] Run decomposition... ✅
[torch.onnx] Translate the graph into ONNX...
[torch.onnx] Translate the graph into ONNX... ✅
正如我們所見,模型無需任何程式碼更改。生成的 ONNX 模型儲存在 torch.onnx.ONNXProgram 中,作為二進位制 protobuf 檔案。
4. 將 ONNX 模型儲存到檔案中#
儘管在許多應用程式中將匯出的模型載入到記憶體中有用,但我們可以使用以下程式碼將其儲存到磁碟:
onnx_program.save("image_classifier_model.onnx")
你可以使用以下程式碼將 ONNX 檔案載入回記憶體並檢查其是否格式正確:
import onnx
onnx_model = onnx.load("image_classifier_model.onnx")
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model)
5. 使用 Netron 視覺化 ONNX 模型圖#
現在我們已經將模型儲存到檔案中,我們可以使用 Netron 視覺化它。Netron 可以在 macos、Linux 或 Windows 計算機上安裝,也可以直接從瀏覽器執行。讓我們透過開啟以下連結來嘗試 Web 版本:https://netron.app/。

Netron 開啟後,我們可以將 image_classifier_model.onnx 檔案拖放到瀏覽器中,或者在點選“開啟模型”按鈕後選擇它。
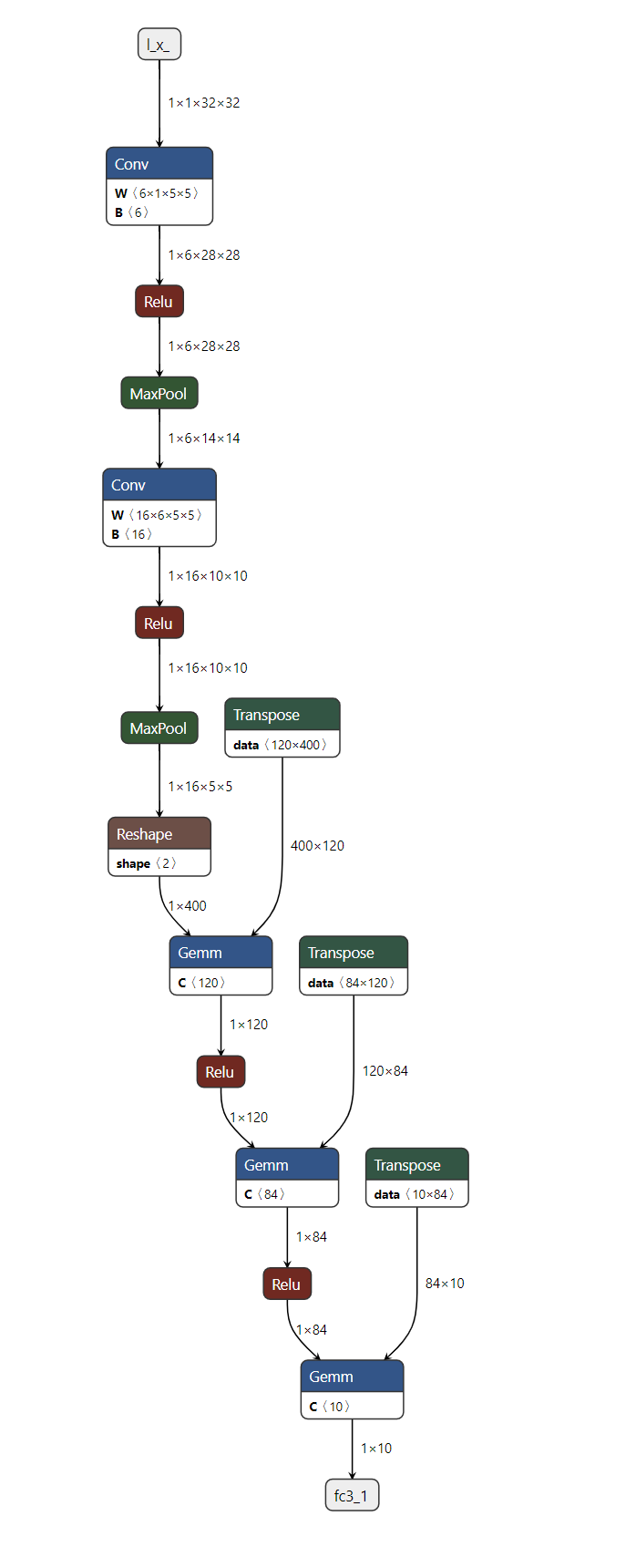
就是這樣!我們已成功將 PyTorch 模型匯出為 ONNX 格式,並使用 Netron 可視化了它。
6. 使用 ONNX Runtime 執行 ONNX 模型#
最後一步是使用 ONNX Runtime 執行 ONNX 模型,但在執行之前,我們先安裝 ONNX Runtime。
pip install onnxruntime
ONNX 標準並不支援 PyTorch 中的所有資料結構和型別,因此我們需要在將 PyTorch 輸入饋送到 ONNX Runtime 之前,將其適配為 ONNX 格式。在我們的示例中,輸入恰好是相同的,但在更復雜的模型中,輸入可能比原始 PyTorch 模型多。
ONNX Runtime 需要一個額外的步驟,包括將所有 PyTorch 張量轉換為 Numpy(在 CPU 上),並將它們包裝在一個字典中,其中鍵是輸入名稱的字串,值為 Numpy 張量。
現在我們可以建立一個 *ONNX Runtime 推理會話*,使用處理後的輸入執行 ONNX 模型並獲取輸出。在本教程中,ONNX Runtime 在 CPU 上執行,但也可以在 GPU 上執行。
import onnxruntime
onnx_inputs = [tensor.numpy(force=True) for tensor in example_inputs]
print(f"Input length: {len(onnx_inputs)}")
print(f"Sample input: {onnx_inputs}")
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(
"./image_classifier_model.onnx", providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
onnxruntime_input = {input_arg.name: input_value for input_arg, input_value in zip(ort_session.get_inputs(), onnx_inputs)}
# ONNX Runtime returns a list of outputs
onnxruntime_outputs = ort_session.run(None, onnxruntime_input)[0]
Input length: 1
Sample input: [array([[[[-0.38049498, 0.609762 , 1.0972704 , ..., 0.7133924 ,
0.4941673 , 0.4716336 ],
[ 0.42390293, -0.05160836, -0.3051912 , ..., 0.780503 ,
-0.68477726, 0.46361122],
[-1.364354 , 0.24252038, -1.1595151 , ..., -1.1784661 ,
-0.7303728 , -0.14575301],
...,
[-0.54219604, 0.82248056, -0.3688359 , ..., -1.3733627 ,
0.62419015, 1.6706848 ],
[ 0.09802157, -0.36778256, -1.6492999 , ..., 0.87087506,
-0.41763693, 0.33648703],
[-0.8979219 , 2.0475664 , 0.1729193 , ..., 0.07267486,
-1.1652538 , 1.0624788 ]]]], dtype=float32)]
7. 比較 PyTorch 的結果與 ONNX Runtime 的結果#
確定匯出模型是否良好的最佳方法是透過與 PyTorch 進行數值評估,PyTorch 是我們的真實來源。
為此,我們需要使用相同的輸入執行 PyTorch 模型,並將結果與 ONNX Runtime 的結果進行比較。在比較結果之前,我們需要將 PyTorch 的輸出轉換為與 ONNX 的格式匹配。
torch_outputs = torch_model(*example_inputs)
assert len(torch_outputs) == len(onnxruntime_outputs)
for torch_output, onnxruntime_output in zip(torch_outputs, onnxruntime_outputs):
torch.testing.assert_close(torch_output, torch.tensor(onnxruntime_output))
print("PyTorch and ONNX Runtime output matched!")
print(f"Output length: {len(onnxruntime_outputs)}")
print(f"Sample output: {onnxruntime_outputs}")
PyTorch and ONNX Runtime output matched!
Output length: 1
Sample output: [[-0.04590763 0.04374031 0.01422022 0.04577638 0.097114 0.05399849
0.06685497 0.09272201 -0.05992632 -0.02955653]]
結論#
就這樣!我們已成功將 PyTorch 模型匯出為 ONNX 格式,將模型儲存到磁碟,使用 Netron 查看了它,使用 ONNX Runtime 執行了它,最後將其數值結果與 PyTorch 的進行了比較。
延伸閱讀#
下面的列表引用了從基本示例到高階場景的教程,不一定按列出的順序。您可以隨時跳轉到您感興趣的特定主題,或者坐下來,享受學習 ONNX 匯出器所有知識的樂趣。
指令碼總執行時間: (0 分鐘 1.685 秒)
