注意
轉到末尾 下載完整的示例程式碼。
自定義 Python 運算子#
建立時間:2024 年 6 月 18 日 | 最後更新:2025 年 3 月 19 日 | 最後驗證:2024 年 11 月 5 日
如何將用 Python 編寫的自定義運算子與 PyTorch 整合
如何使用
torch.library.opcheck測試自定義運算子
PyTorch 2.4 或更高版本
PyTorch 提供了一個大型運算子庫,可用於 Tensor(例如 torch.add、torch.sum 等)。但是,您可能希望使用 PyTorch 的新自定義運算子,也許是由第三方庫編寫的。本教程將展示如何包裝 Python 函式,使其行為類似於 PyTorch 的原生運算子。您可能希望在 PyTorch 中建立自定義運算子的原因包括:
將任意 Python 函式視為對
torch.compile不透明的可呼叫物件(即,阻止torch.compile跟蹤該函式)。為任意 Python 函式新增訓練支援
使用 torch.library.custom_op() 建立 Python 自定義運算子。使用 C++ TORCH_LIBRARY API 建立 C++ 自定義運算子(這些在無 Python 的環境中工作)。有關更多詳細資訊,請參閱 自定義運算子登陸頁面。
請注意,如果您的操作可以表示為現有 PyTorch 運算子的組合,那麼通常不需要使用自定義運算子 API — 所有內容(例如 torch.compile、訓練支援)都應該可以正常工作。
示例:將 PIL 的 crop 包裝成自定義運算子#
假設我們正在使用 PIL 的 crop 操作。
import torch
from torchvision.transforms.functional import to_pil_image, pil_to_tensor
import PIL
import IPython
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def crop(pic, box):
img = to_pil_image(pic.cpu())
cropped_img = img.crop(box)
return pil_to_tensor(cropped_img).to(pic.device) / 255.
def display(img):
plt.imshow(img.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0)))
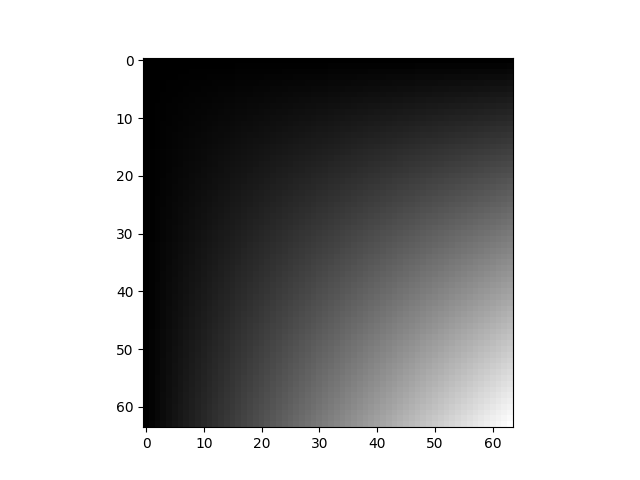
img = torch.ones(3, 64, 64)
img *= torch.linspace(0, 1, steps=64) * torch.linspace(0, 1, steps=64).unsqueeze(-1)
display(img)
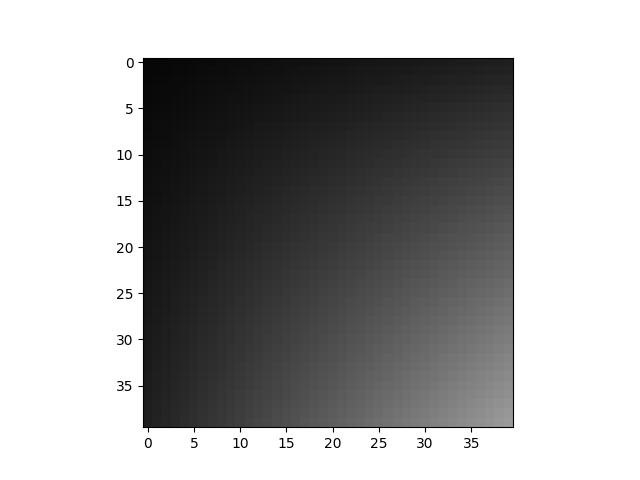
cropped_img = crop(img, (10, 10, 50, 50))
display(cropped_img)
torch.compile 預設情況下無法有效處理 crop:torch.compile 會在它無法處理的函式上引發“圖中斷”,而圖中斷不利於效能。下面的程式碼透過引發錯誤來演示這一點(torch.compile 配合 fullgraph=True 在發生圖中斷時會引發錯誤)。
為了將 crop 黑盒化以供 torch.compile 使用,我們需要做兩件事:
將函式包裝成 PyTorch 自定義運算子。
為該運算子新增一個“
FakeTensor核心”(也稱為“元核心”)。給定一些FakeTensors輸入(不具有儲存的虛擬 Tensor),此函式應返回您選擇的具有正確 Tensor 元資料(形狀/步幅/dtype/裝置)的虛擬 Tensor。
from typing import Sequence
# Use torch.library.custom_op to define a new custom operator.
# If your operator mutates any input Tensors, their names must be specified
# in the ``mutates_args`` argument.
@torch.library.custom_op("mylib::crop", mutates_args=())
def crop(pic: torch.Tensor, box: Sequence[int]) -> torch.Tensor:
img = to_pil_image(pic.cpu())
cropped_img = img.crop(box)
return (pil_to_tensor(cropped_img) / 255.).to(pic.device, pic.dtype)
# Use register_fake to add a ``FakeTensor`` kernel for the operator
@crop.register_fake
def _(pic, box):
channels = pic.shape[0]
x0, y0, x1, y1 = box
result = pic.new_empty(y1 - y0, x1 - x0, channels).permute(2, 0, 1)
# The result should have the same metadata (shape/strides/``dtype``/device)
# as running the ``crop`` function above.
return result
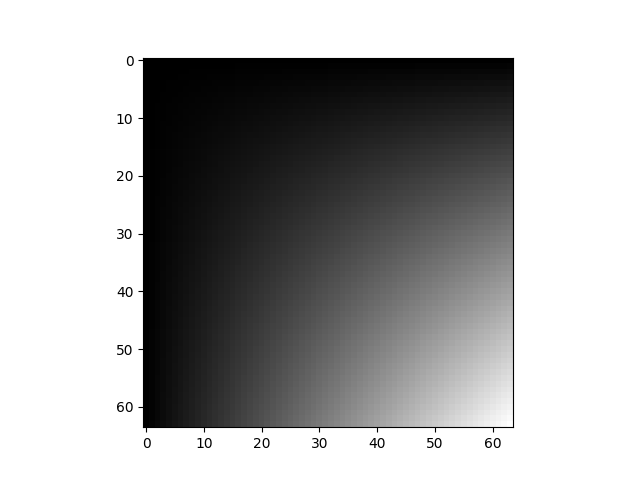
完成此操作後,crop 將不再有圖中斷。
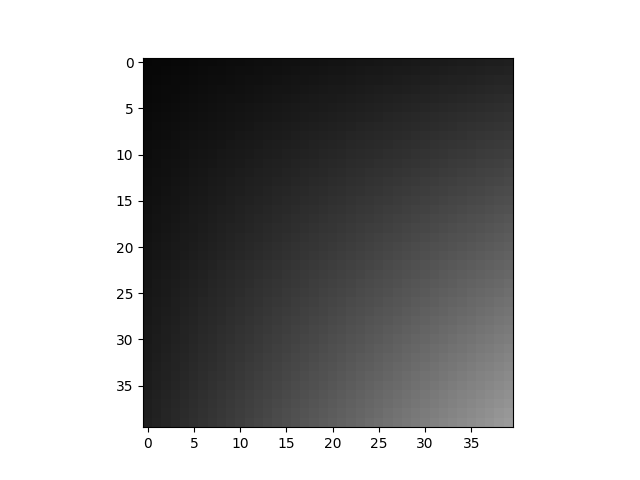
display(cropped_img)
為 crop 新增訓練支援#
使用 torch.library.register_autograd 為運算子新增訓練支援。優先使用此方法,而不是直接使用 torch.autograd.Function;某些 autograd.Function 與 PyTorch 運算子註冊 API 的組合可能會導致(並且已經導致)與 torch.compile 組合時出現靜默不正確的情況。
如果您不需要訓練支援,則無需使用 torch.library.register_autograd。如果您最終使用沒有自動微分註冊的 custom_op 進行訓練,我們將發出錯誤訊息。
crop 的梯度公式本質上是 PIL.paste(我們將推導過程留給讀者作為練習)。首先,我們將 paste 包裝成一個自定義運算子。
@torch.library.custom_op("mylib::paste", mutates_args=())
def paste(im1: torch.Tensor, im2: torch.Tensor, coord: Sequence[int]) -> torch.Tensor:
assert im1.device == im2.device
assert im1.dtype == im2.dtype
im1_pil = to_pil_image(im1.cpu())
im2_pil = to_pil_image(im2.cpu())
PIL.Image.Image.paste(im1_pil, im2_pil, coord)
return (pil_to_tensor(im1_pil) / 255.).to(im1.device, im1.dtype)
@paste.register_fake
def _(im1, im2, coord):
assert im1.device == im2.device
assert im1.dtype == im2.dtype
return torch.empty_like(im1)
現在,我們使用 register_autograd 來指定 crop 的梯度公式。
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
grad_input = grad_output.new_zeros(ctx.pic_shape)
grad_input = paste(grad_input, grad_output, ctx.coords)
return grad_input, None
def setup_context(ctx, inputs, output):
pic, box = inputs
ctx.coords = box[:2]
ctx.pic_shape = pic.shape
crop.register_autograd(backward, setup_context=setup_context)
請注意,反向傳播必須是 PyTorch 可理解的運算子的組合,這就是為什麼我們將 paste 包裝成自定義運算子,而不是直接使用 PIL 的 paste。
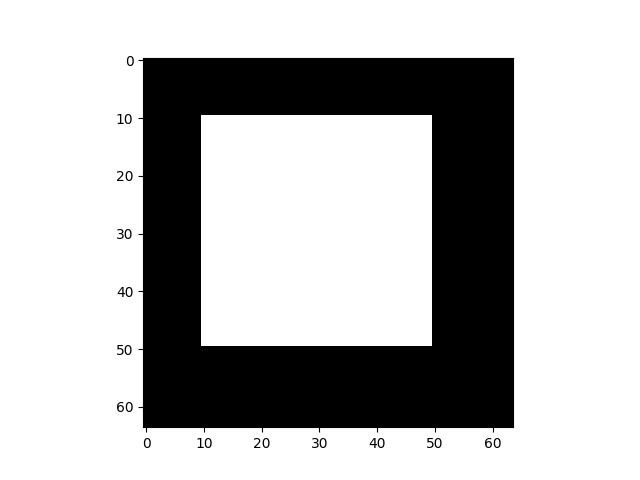
這是正確的梯度,在裁剪區域為 1(白色),在未使用區域為 0(黑色)。
測試 Python 自定義運算子#
使用 torch.library.opcheck 測試自定義運算子是否已正確註冊。這不會測試梯度在數學上是否正確;請為此編寫單獨的測試(手動測試或使用 torch.autograd.gradcheck)。
要使用 opcheck,請向其傳遞一組示例輸入進行測試。如果您的運算子支援訓練,則示例應包含需要 grad 的 Tensor。如果您的運算子支援多個裝置,則示例應包含來自每個裝置的 Tensor。
examples = [
[torch.randn(3, 64, 64), [0, 0, 10, 10]],
[torch.randn(3, 91, 91, requires_grad=True), [10, 0, 20, 10]],
[torch.randn(3, 60, 60, dtype=torch.double), [3, 4, 32, 20]],
[torch.randn(3, 512, 512, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.double), [3, 4, 32, 45]],
]
for example in examples:
torch.library.opcheck(crop, example)
可變 Python 自定義運算子#
您還可以包裝一個可變輸入的 Python 函式作為自定義運算子。可變輸入的函式很常見,因為許多底層核心就是這樣編寫的;例如,一個計算 sin 的核心可能接收輸入和輸出張量,並將 input.sin() 寫入輸出張量。
我們將使用 numpy.sin 來演示可變 Python 自定義運算子的示例。
import numpy as np
@torch.library.custom_op("mylib::numpy_sin", mutates_args={"output"}, device_types="cpu")
def numpy_sin(input: torch.Tensor, output: torch.Tensor) -> None:
assert input.device == output.device
assert input.device.type == "cpu"
input_np = input.numpy()
output_np = output.numpy()
np.sin(input_np, out=output_np)
由於該運算子不返回任何內容,因此無需註冊 FakeTensor 核心(元核心)即可使其與 torch.compile 一起使用。
@torch.compile(fullgraph=True)
def f(x):
out = torch.empty(3)
numpy_sin(x, out)
return out
x = torch.randn(3)
y = f(x)
assert torch.allclose(y, x.sin())
這是 opcheck 的執行結果,告訴我們確實正確註冊了該運算子。opcheck 會在您忘記將輸出新增到 mutates_args 時出錯,例如。
example_inputs = [
[torch.randn(3), torch.empty(3)],
[torch.randn(0, 3), torch.empty(0, 3)],
[torch.randn(1, 2, 3, 4, dtype=torch.double), torch.empty(1, 2, 3, 4, dtype=torch.double)],
]
for example in example_inputs:
torch.library.opcheck(numpy_sin, example)
結論#
在本教程中,我們學習瞭如何使用 torch.library.custom_op 在 Python 中建立自定義運算子,該運算子可與 torch.compile 和 autograd 等 PyTorch 子系統配合使用。
本教程提供了自定義運算子的基本介紹。有關更多詳細資訊,請參閱:
指令碼總執行時間: (0 分鐘 3.593 秒)



