DeviceMesh 入門#
建立日期:2024 年 1 月 24 日 | 最後更新:2025 年 7 月 18 日 | 最後驗證:2024 年 11 月 5 日
注意
 在 github 上檢視和編輯此教程。
在 github 上檢視和編輯此教程。
先決條件
Python 3.8 - 3.11
PyTorch 2.2
設定分散式通訊器,例如 NVIDIA Collective Communication Library (NCCL) 通訊器,用於分散式訓練可能是一個重大的挑戰。對於使用者需要組合不同並行策略的工作負載,使用者需要為每種並行策略手動設定和管理 NCCL 通訊器(例如,ProcessGroup)。這個過程可能很複雜且容易出錯。DeviceMesh 可以簡化這個過程,使其更易於管理且不易出錯。
什麼是 DeviceMesh#
DeviceMesh 是一個管理 ProcessGroup 的更高級別抽象。它允許使用者輕鬆建立跨節點和節點內程序組,而無需擔心如何為不同的子程序組正確設定 rank。使用者還可以透過 DeviceMesh 輕鬆管理多維並行底層的 process_groups/devices。
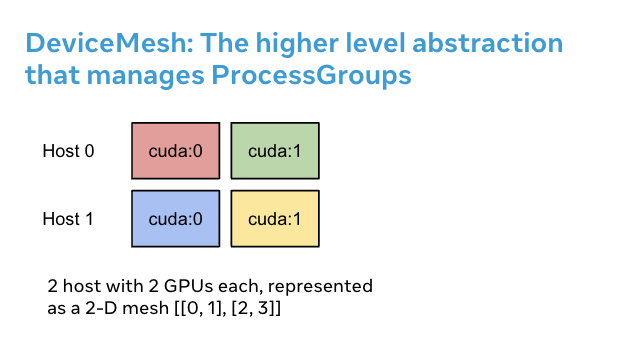
DeviceMesh 有何用處#
當處理需要並行組合的多維並行(即 3D 並行)時,DeviceMesh 會很有用。例如,當您的並行策略同時需要跨主機和主機內的通訊時。上圖顯示,我們可以建立一個 2D mesh,連線每個主機內的裝置,並在同構設定中將每個裝置與另一臺主機上的對應裝置連線起來。
在沒有 DeviceMesh 的情況下,使用者在應用任何並行策略之前,需要手動設定每個程序上的 NCCL 通訊器和 cuda 裝置,這可能相當複雜。下面的程式碼片段說明了在沒有 DeviceMesh 的情況下進行混合分片 2D 並行模式設定。首先,我們需要手動計算分片組和複製組。然後,我們需要將正確的分片組和複製組分配給每個 rank。
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
# Understand world topology
rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
print(f"Running example on {rank=} in a world with {world_size=}")
# Create process groups to manage 2-D like parallel pattern
dist.init_process_group("nccl")
torch.cuda.set_device(rank)
# Create shard groups (e.g. (0, 1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6, 7))
# and assign the correct shard group to each rank
num_node_devices = torch.cuda.device_count()
shard_rank_lists = list(range(0, num_node_devices // 2)), list(range(num_node_devices // 2, num_node_devices))
shard_groups = (
dist.new_group(shard_rank_lists[0]),
dist.new_group(shard_rank_lists[1]),
)
current_shard_group = (
shard_groups[0] if rank in shard_rank_lists[0] else shard_groups[1]
)
# Create replicate groups (for example, (0, 4), (1, 5), (2, 6), (3, 7))
# and assign the correct replicate group to each rank
current_replicate_group = None
shard_factor = len(shard_rank_lists[0])
for i in range(num_node_devices // 2):
replicate_group_ranks = list(range(i, num_node_devices, shard_factor))
replicate_group = dist.new_group(replicate_group_ranks)
if rank in replicate_group_ranks:
current_replicate_group = replicate_group
為了執行上面的程式碼片段,我們可以利用 PyTorch Elastic。讓我們建立一個名為 2d_setup.py 的檔案。然後,執行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --rdzv_id=100 --rdzv_endpoint=localhost:29400 2d_setup.py
注意
為了演示的簡潔性,我們僅使用一個節點來模擬 2D 並行。請注意,此程式碼片段也可用於多主機設定。
藉助 init_device_mesh(),我們只需兩行程式碼即可完成上述 2D 設定,並且如果需要,我們仍然可以訪問底層的 ProcessGroup。
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
mesh_2d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 4), mesh_dim_names=("replicate", "shard"))
# Users can access the underlying process group thru `get_group` API.
replicate_group = mesh_2d.get_group(mesh_dim="replicate")
shard_group = mesh_2d.get_group(mesh_dim="shard")
讓我們建立一個名為 2d_setup_with_device_mesh.py 的檔案。然後,執行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 2d_setup_with_device_mesh.py
如何將 DeviceMesh 與 HSDP 結合使用#
混合分片資料並行 (HSDP) 是一種在主機內執行 FSDP,在主機間執行 DDP 的 2D 策略。
讓我們透過一個簡單的設定示例,看看 DeviceMesh 如何幫助您將 HSDP 應用到模型中。有了 DeviceMesh,使用者就不需要手動建立和管理分片組和複製組。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
from torch.distributed.fsdp import fully_shard as FSDP
class ToyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ToyModel, self).__init__()
self.net1 = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.net2 = nn.Linear(10, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net2(self.relu(self.net1(x)))
# HSDP: MeshShape(2, 4)
mesh_2d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 4), mesh_dim_names=("dp_replicate", "dp_shard"))
model = FSDP(
ToyModel(), device_mesh=mesh_2d
)
讓我們建立一個名為 hsdp.py 的檔案。然後,執行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 hsdp.py
如何為自定義並行解決方案使用 DeviceMesh#
在進行大規模訓練時,您可能需要更復雜的自定義並行訓練組合。例如,您可能需要為不同的並行解決方案切分子 mesh。DeviceMesh 允許使用者從父 mesh 中切分子 mesh,並重用父 mesh 初始化時已建立的 NCCL 通訊器。
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
mesh_3d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 2, 2), mesh_dim_names=("replicate", "shard", "tp"))
# Users can slice child meshes from the parent mesh.
hsdp_mesh = mesh_3d["replicate", "shard"]
tp_mesh = mesh_3d["tp"]
# Users can access the underlying process group thru `get_group` API.
replicate_group = hsdp_mesh["replicate"].get_group()
shard_group = hsdp_mesh["shard"].get_group()
tp_group = tp_mesh.get_group()
結論#
總而言之,我們已經瞭解了 DeviceMesh 和 init_device_mesh(),以及如何使用它們來描述叢集中裝置的佈局。
更多資訊,請參閱以下內容



